No content results match your keyword.
Content
You have successfully logged out.
Not registered yet?
Total intravenous anesthesia (TIVA)
TIVA is a technique of general anesthesia which uses a combination of agents given via syringe pump exclusively by the intravenous route without the use of inhalation agents (Gas Anesthesia).1 There is a solid rationale for the use of TIVA in some patient cases where the delivery of inhaled anesthetics is impossible or disadvantageous, or in scenarios where traditional anesthetic delivery systems may be unavailable or impractical. In other cases, the use of TIVA could make the process more efficient and advantageous for the patient.
Our Spaceplus Perfusor® visualizes the status of the anesthesia via a graphical overview as a user-friendly technique for the caregivers. The user interface can be flexibly adapted to specific TCI settings to reduce handling steps.
Target Controlled Infusion (TCI) is a standardized infusion technique for the administration of opioids, propofol and other anesthetics in anesthesia.
TCI comprises the implementation of pharmacologic models in infusion pumps. These “TCI pumps” control the infusion rates in order to reach and maintain predefined concentrations or targets.
In the case of anesthesia, the target is identified through specific algorithms. The infusion rates that are required to reach and maintain the target concentration are based on pharmacokinetic models.
These targets can either be plasma concentrations referred to as “Plasma Mode“ or “Plasma Targeting“ or effect-site concentrations referred to as “Effect(-site) Mode“ or “Effect(-site) Targeting“.
Compared generally to traditional volatile anesthetic techniques,TIVA/TCI offer several potential advantages. These include:
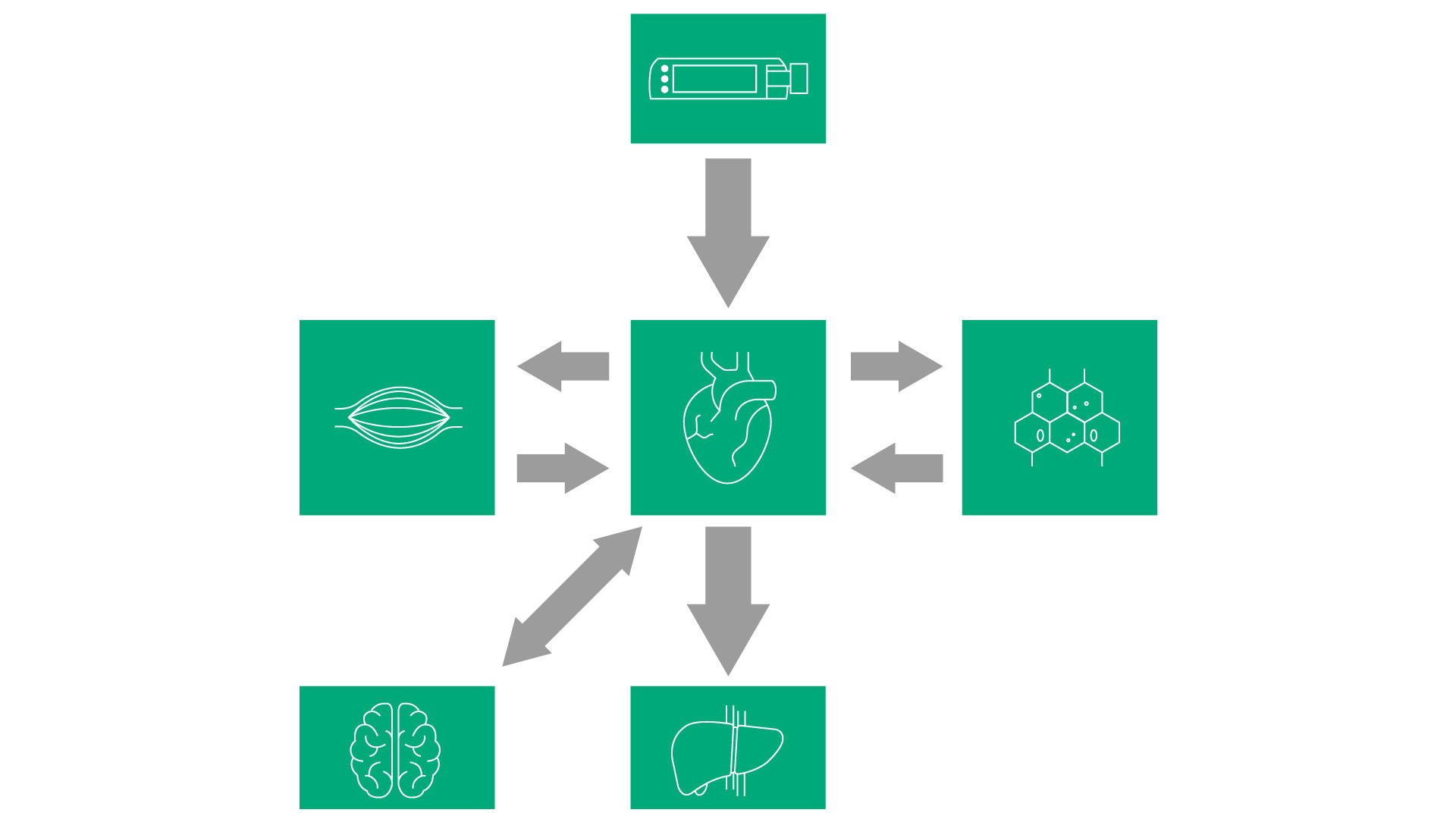
Many TCI models are pure pharmacokinetic models utilizing three compartments:
1. A central compartment (usually representing the blood plasma)
2. A rapidly equilibrating compartment (representing well perfused tissues like muscles)
3. A slowly equilibrating compartment (representing less well perfused tissues, like fatty tissue)
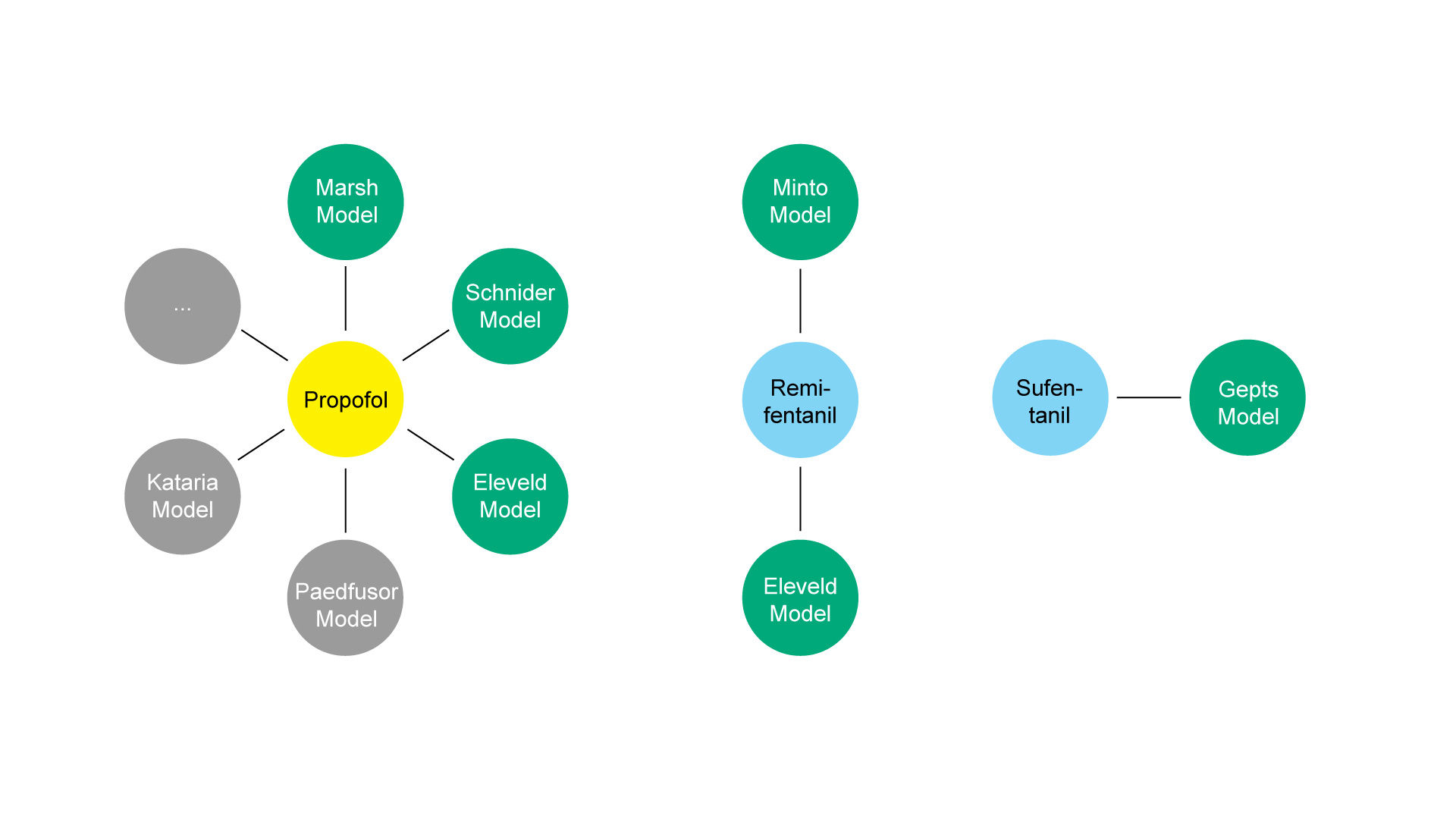
TCI models are available for various anesthetic drugs. For many drugs there are even different TCI models available. They vary in terms of the required input of patient characteristics (e.g. like body weight, sex, height, age, etc.), and the population that was used to generate the models. There are specific models for children, adults, obese patients etc. Some models are based on only small patient populations others are based on wide populations.
With Space®plus the following TCI models are available:
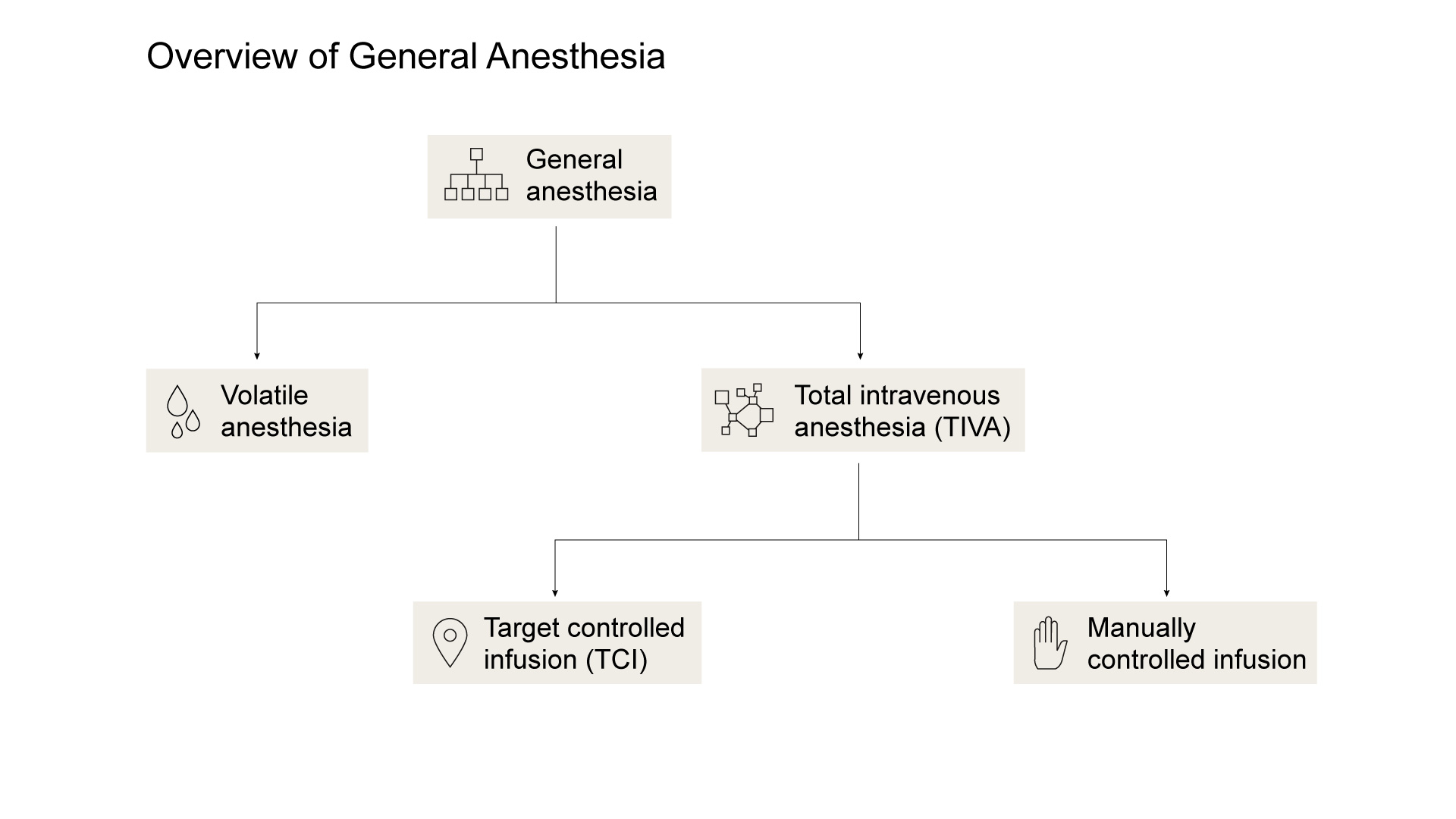
is typically applied through tracheal or laryngeal tubes. These are connected to an anesthetic vaporizer and an anesthesia machine. Typical agents are isoflurane, sevoflurane and desflurane.
/
Total intravenous anesthesia (TIVA) is a technique of general anesthesia which uses a combination of agents given via syringe pump exclusively by the intravenous route without the use of inhalation agents (Gas Anesthesia).2
/
Target Controlled Infusion (TCI)3 is an algorithm based userfriendly technique for the caregiver. It is the clinical application of pharmacologic models to support the infusion of (anesthesiologic) drugs.
/
Do you need a demo or would you like to learn more about the Space®plus infusion system? Write to us and we will be happy to help you!
We will contact you shortly.
References